TDengine is excited to announce support for connecting TDengine TSDB with Ontop as well as a partnership with Ontopic. Ontop is an open-source virtual knowledge graph system that dynamically transforms database content into knowledge graphs without requiring data migration from the original source.
This integration combines the strong logical reasoning of knowledge graphs with the generalization capabilities of large language models, providing intelligent analysis solutions with cognitive capabilities for complex IoT scenarios such as device failure root cause analysis and energy efficiency optimization.

The integration of TDengine TSDB and Ontop achieves the following:
- Automatic conversion of time-series data to RDF, supporting SPARQL semantic queries.
- Unified data access interface compliant with W3C standards.
- Unlocking knowledge graph analysis and reasoning capabilities for industrial IoT.
Prerequisites
- Install TDengine TSDB 3.3.6.0 or later. TDengine TSDB-OSS and TSDB-Enterprise are both supported. For installation instructions, visit our Download Center.
- Ensure that TDengine TSDB and taosAdapter are running.
- Download the TDengine JDBC Client Library 3.6.0 or later. Select the file ending in
dist.jar. - Download and build the
version5branch of the Ontop source code according to the readme file.
Configure Data Source
-
Copy the TDengine JDBC client library in the
jdbc/directory within Ontop. -
In the Ontop
.propertiesfile, configure the JDBC connection:jdbc.url = jdbc:TAOS-WS://<taosadapter-host>:<port>/<database> jdbc.user = <tdengine-username> jdbc.password = <tdengine-password> jdbc.driver = com.taosdata.jdbc.ws.WebSocketDriverFor URL parameter details, see TDengine URL Specification.
-
Define the mapping relationship between TDengine TSDB and Ontop in the
.obdafile. A smart meter scenario is given as an example.[PrefixDeclaration] : http://example.org/tde ns: http://example.org/ns# [MappingDeclaration] @collection [[ mappingId meters-mapping target ns:{ts} a ns:Meters ; ns:ts {ts} ; ns:voltage {voltage}; ns:phase {phase}; ns:groupid {groupid}; ns:location {location}^^xsd:string . source SELECT ts, voltage, phase, groupid, location from test.meters ]]Format Description:
Key Field Description mappingId Mapping ID, uniquely identifies the mapping relationship source TDengine TSDB SQL query statement (supports complex queries) target Field mapping relationship (uses default conversion rules when type not specified) You can specify mapping data types in the target. If not specified, the following conversion rules apply:
TDengine JDBC Data Type Ontop Data Type java.sql.Timestamp xsd:datetime java.lang.Boolean xsd:boolean java.lang.Byte xsd:byte java.lang.Short xsd:short java.lang.Integer xsd:int java.lang.Long xsd:long java.math.BigInteger xsd:nonNegativeInteger java.lang.Float xsd:float java.lang.Double xsd:double byte[] xsd:base64Binary java.lang.String xsd:string java.math.BigDecimal xsd:decimal For complete
.obdafile format documentation, refer to Ontop OBDA Documentation. -
Start the Ontop endpoint service to verify configuration:
ontop endpoint -p db.properties -m db.obda --port 8080
In a web browser, access http://localhost:8080. If the SPARQL query interface appears, the configuration is successful.
Sample Scenario
In this scenario, smart meter data from a residential community is stored in TDengine TSDB. Ontop is used to transform this data into a virtual knowledge graph and identify overloaded equipment with voltage exceeding 240V.
Data Preparation
-
Generate simulated data using taosBenchmark:
taosBenchmark -t 100 -n 1000 -y -
Edit the Ontop .properties file and configure the connection:
jdbc.url=jdbc:TAOS-WS://localhost:6041/test jdbc.user=root jdbc.password=taosdata jdbc.driver=com.taosdata.jdbc.ws.WebSocketDriver -
Edit the Ontop .odba file and configure the table mapping:
[PrefixDeclaration] : http://example.org/tde ns: http://example.org/ns# [MappingDeclaration] @collection [[ mappingId meters-mapping target ns:{ts} a ns:Meters ; ns:ts {ts} ; ns:voltage {voltage}; ns:phase {phase}; ns:groupid {groupid}; ns:location {location}^^xsd:string . source SELECT ts, voltage, phase, groupid, location from test.meters ]] -
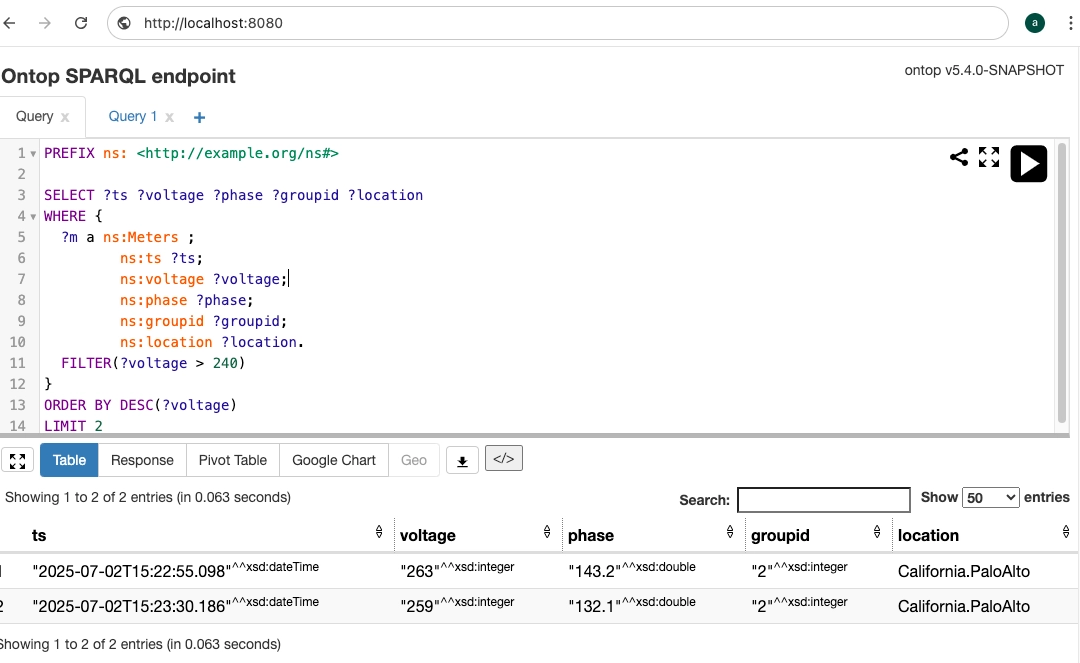
Create a SPARQL query statement to query smart meter devices with voltage exceeding 240V and display the top two results by voltage in descending order:
PREFIX ns: <http://example.org/ns#> SELECT ?ts ?voltage ?phase ?groupid ?location WHERE { ?m a ns:Meters ; ns:ts ?ts; ns:voltage ?voltage; ns:phase ?phase; ns:groupid ?groupid; ns:location ?location. FILTER(?voltage > 240) } ORDER BY DESC(?voltage) LIMIT 2 -
In a web browser, open the Ontop SPARQL endpoint and run the SPARQL statement.

Results are returned in SPARQL JSON format, containing meter collection timestamps, voltage readings, phase, group ID, and device location information.
{
"head" : {
"vars" : [
"ts",
"voltage",
"phase",
"groupid",
"location"
]
},
"results" : {
"bindings" : [
{
"ts" : {
"datatype" : "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#dateTime",
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "2025-07-02T15:22:55.098"
},
"voltage" : {
"datatype" : "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#integer",
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "263"
},
"phase" : {
"datatype" : "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#double",
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "143.2"
},
"groupid" : {
"datatype" : "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#integer",
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "2"
},
"location" : {
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "California.PaloAlto"
}
},
{
"ts" : {
"datatype" : "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#dateTime",
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "2025-07-02T15:23:30.186"
},
"voltage" : {
"datatype" : "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#integer",
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "259"
},
"phase" : {
"datatype" : "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#double",
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "132.1"
},
"groupid" : {
"datatype" : "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#integer",
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "2"
},
"location" : {
"type" : "literal",
"value" : "California.PaloAlto"
}
}
]
}
}